
After launching the first series of premium laptops equipped with Snapdragon X Elite processors earlier this year, Qualcomm has unveiled a mid-range version of ARM architecture-based processors called X Plus.
The octa-core Snapdragon X Plus model was introduced for budget laptops to meet the artificial intelligence requirements of CoPilot Plus computers. Now the performance of this processor has been examined at the IFA 2024 exhibition.
Qualcomm presented two versions of its octa-core processor in separate laptop bodies: one is the Qualcomm reference laptop with the X1P-46-100 chip, and the other is the Asus Vivobook S15 model equipped with the X1P-42-100 chip.
|
Qualcomm Reference Design |
ASUS Vivobook S15 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Processor |
X1P-46-100 |
X1P-42-100 |
|
The number of cores |
8 |
8 |
|
Boost frequency |
4 GHz single-core and 3.4 GHz multi-core |
3.2 GHz single-core and 3.4 GHz multi-core |
|
GPU speed |
2.1 teraflops |
1.7 teraflops |
|
NPU power |
45 tops |
45 tops |
As expected, the reduction in the number of CPU cores from 12 Orion cores in the X Elite to 8 cores in the smaller X Plus model greatly affects the processor’s multi-core performance.
The X1P-42-100 processor appeared about 25% slower than the flagship model in the Geekbench 6 benchmark, and about 45% behind in CineBench 2024, which is likely due to its 30MB cache compared to the X Elite’s 42MB cache.
|
Geekbench 6 |
Cinebench R24 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Processor |
single core |
multi-core |
single core |
multi-core |
|
Intel i9-13980HX |
2,881 |
17,564 |
117 |
1495 |
|
SD X Elite (80W) |
2971 |
15,371 |
131 |
1229 |
|
Apple M2 Max |
2692 |
14,863 |
121 |
1025 |
|
SD X Elite (23W) |
2780 |
14,029 |
123 |
1022 |
|
SD X Plus (X1P-46-100) |
2614 |
11,884 |
116 |
733 |
|
SD X Plus (X1P-42-100) |
2422 |
11,260 |
108 |
659 |
|
Apple M2 |
2621 |
10,063 |
120 |
555 |
The single-core performance of Snapdragon X Plus processors differ greatly due to the difference in their boost frequency. The single-core score of X1P-42-100, the weakest model of the X Plus series, is about 22% and the score of X1P-46 is about 13% behind the Snapdragon X Elite at its maximum power consumption.
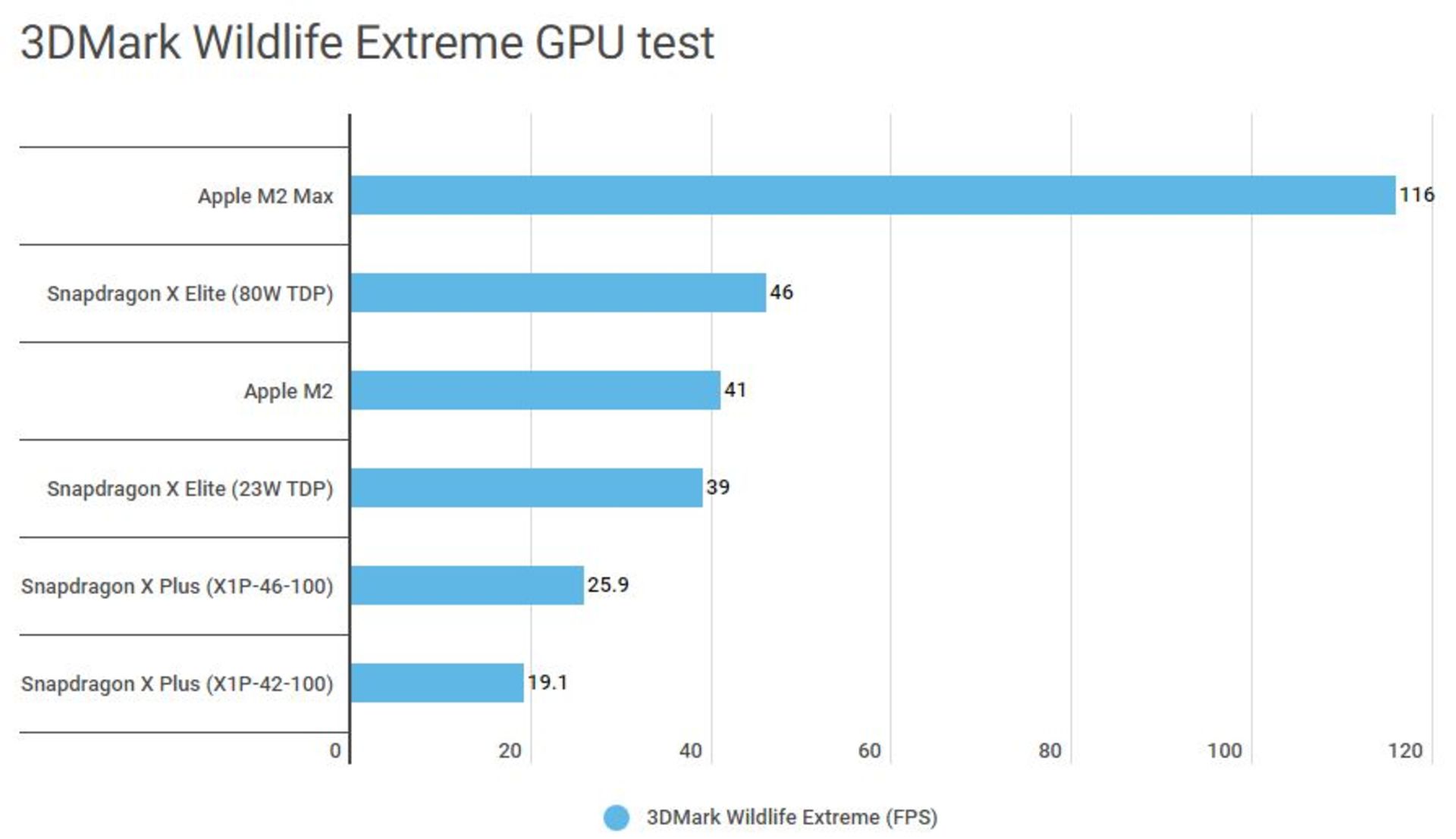
In graphics processing, the Adreno units of the octa-core X Plus processors are much weaker than the X Elite (1.7 and 2.1 teraflops compared to 3.8 teraflops) and are far from it.
Android Authority
Mid-range Snapdragon X Plus processors compete with the Apple M2 chip in Apple’s MacBook Air in terms of single-core performance, and surpass it in multi-core processing.
However, the powerful eight-core GPU of the MacBook Air in the 3DMark graphics test decisively distanced itself from all members of the Snapdragon X family. Apple’s M2 internal graphics deliver several times the performance of Qualcomm’s budget chips, making the MacBook Air a more capable gaming platform.
When buying ARM laptops based on Qualcomm processors, you should pay attention to the type of chip used in the device. The price of the Asus Vivobook S15 laptop reviewed here is $1,300, which is not very affordable considering its low-end processor performance. However, you can buy a Microsoft Surface Laptop equipped with Snapdragon X Elite for $999, which has a much more powerful processor.









